Executing SQL Queries
Please be careful when using SQL with user input - SQL injections are a real bummer :(. Consider using Prepared Queries where possible.
Retrieving data
Once you've established a connection to your database, the next thing you'll probably want to do is execute a SQL query that retrieves something from the database. We'll only be covering regular queries here, but the basic principle is the same. For prepared queries, please read the Prepared Queries section after you've finished this section.
So to execute a SQL query, drag out of your "Connect to PostgreSQL database" node, and place the "Execute Query" node. This node will allow you to execute SQL queries, and get data back from them.
I'll assume you know the basics of SQL from now on, but if not, I'd highly recommend PostgreSQL's official resource on this which can be found here. Now I've created a basic table containing an id (SERIAL), and a username (STRING). I've created a few sample records, including the following:
| id | username |
|---|---|
| 10 | HowToCompute |
Now to get my username, I'd use the following SQL query:
SELECT (username) FROM test WHERE id = 10;
The great thing about using regular queries is that we can literally copy this over to the "Query" parameter of our "Execute Query" node, as can be seen below:
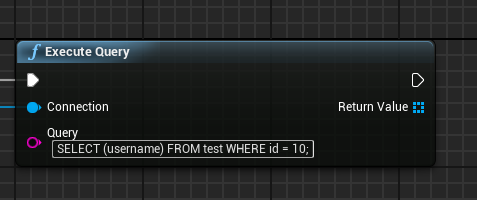
Now when this node gets called with a connected database, it will execute the query, and return any values it retrieves from the database.
These "values" we're talking about are actually rows, and contain data in cells (which we will call columns to comply with convention). To iterate over the rows, we can use a Foreach Loop, as can be seen below (NOTE: in our example, we will only have a single row):
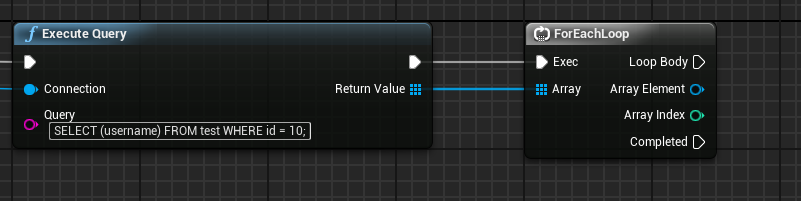
This loop will iterate over all of the returned rows, allowing you to access the properties it contains. To access these properties, drag out of the Array Element pin and use any of the Get Row Column As nodes. If you're unsure about the returned type, you can also use the Get Row Column Type node - this will tell you the type if NetDB recognizes it. As of writing, the following getters exist:
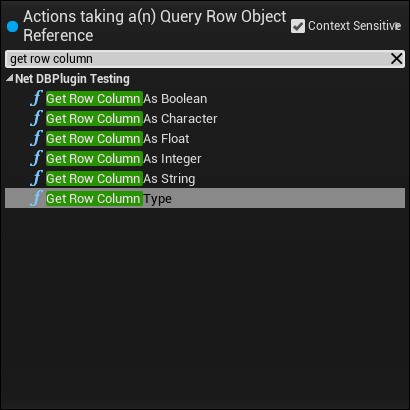
All of the Get Row Column nodes provided by NetDB have a parameter called column name, this allows you to specify which column/cell the value should be retrieved from. If you recall our example from above, this will be the "username" column. Putting this all together, we'd end up with something like the nodes below:
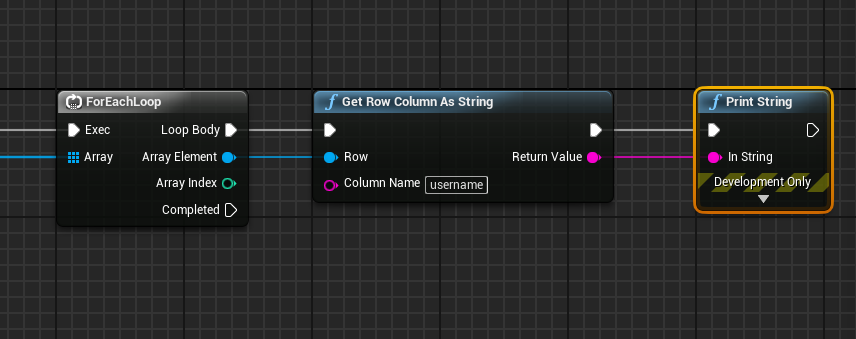
This covers the basics of retrieving records out of the database! We highly recommend taking a look at the Prepared Queries section below if you're dealing with any data the user can modify for security reasons. Using SQL with user input could leave your game vulnerable to a SQL Injection, which allows hackers to delete tables/databases, steal the data contained within, or worse!
Inserting data
Now that you know how to retrieve records from the database, inserting them is simple! If you recall our example with an id and username from above, we would now like to insert a new username. Since our id is SERIAL, it will automatically create a new number for every username we insert. To create a new user, we'll only need to provide the username (say, our good friend, foobar), so in SQL terms:
INSERT INTO test (username) VALUES ('foobar');
To do this inside of UE4, start by dragging out of the “Connect to PostgreSQL database” node, and placing another “Execute Query” node. As before, as this isn’t a prepared query, we can simply copy that statement into the “Query” field. You can see the above example implemented in UE4 below:
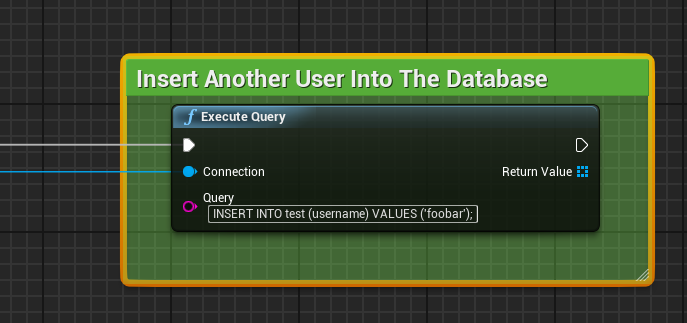
And since we’re only inserting a record into the database, and not asking it to return anything, we don’t need to do anything else! As before, please note that when dealing with anything the user can influence, you should seriously consider using Prepared Queries to avoid the risk of a SQL Injection.