Bare-bones Workflow
"Bare Bones" Workflow
As mentioned before, the "Bare Bones" workflow should be used with extreme caution. I'll start off with describing some common pitfalls of this approach.
The "Bare Bones" workflow gives you complete power over the way you use the TCP or secured TCP sockets. But just like the popular saying: "with great power comes great responsibility", this means you have complete responsibility for the socket too.
In practical terms: you're in charge of closing the socket, ensuring there is data to be read before trying to read it, etc. Failing to do so can cause your game to hang, or worse: crash as a whole. For this reason, as well as the fact that the managed approach is more easy, we highly recommend opting for that workflow. At the very least, we recommend having (basic) experience with POSIX sockets, and we won't be covering the little details, since we're assuming you're already aware of those.
I'll list all of the nodes below with a short description/a few notes. This should help you getting started using them.
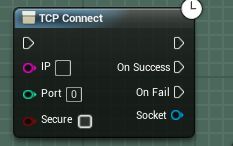
The TCP connect node will connect to an IP address and port, and then execute the OnSuccess or OnFail pin depending on its success at connecting. The Secure checkbox allows you to toggle SSL on or off.
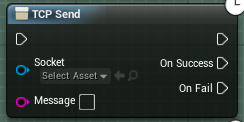
The TCP Send node needs a valid socket, and a message to send. If you'd like to send a byte array, please use the Bytes to String node. If the message is successfully sent, you the OnSuccess pin will be fired, if something goes wrong, the OnFail pin will be fired.
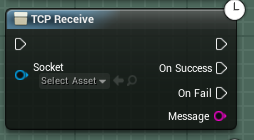
The TCP receive node takes in a valid socket, and will attempt to read data from it. If it successfully manages to do this, it will fire the OnSuccess pin, setting a message for you to use, but if it hits a snag, or no data is set, it will execute the OnFail code. Please ensure you do NOT use the Message variable within your OnFail code as this will contain an invalid string.
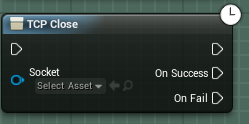
When you're done with a socket, you'll need to close it. The TCP close will take in a valid socket, and attempt to close it. The OnSuccess pin will be fired if it successfully closes the socket, and the OnFail pin will be fired if there were any issues in closing the socket.